The Tchebycheff Approach
Tchebycheff Approach
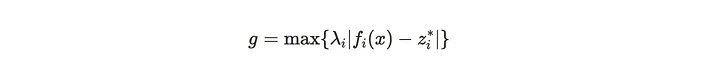
On a philosophical level, this formula represents a pursuit of balance, fairness, or optimization in the face of competing priorities. It embodies several key philosophical ideas:
1. Maximizing the Greatest Discrepancy
By focusing on the maximum discrepancy (or error), the formula suggests prioritizing the “worst-off” scenario or the most critical deviation from an ideal. This aligns with the philosophical principle of minimax, often used in ethical theories and decision-making to minimize the worst possible outcome.
2. Weighted Values and Importance (λᵢ)
The inclusion of (λᵢ) reflects the idea that not all differences or deviations are equally important. Some aspects of reality may deserve more attention, weight, or significance. This resonates with value pluralism, the notion that different priorities must coexist and be carefully balanced.
3. Absolute Value and Objectivity
The absolute value ensures that the formula considers only the magnitude of deviation, not the direction. Philosophically, this reflects a commitment to objectivity—it doesn’t matter whether you overachieve or underachieve, the focus is on how far you are from the ideal.
4. Tension Between Reality and Ideal (fᵢ(x) - zᵢ*)
The difference f_i(x) - z_i* encapsulates a core philosophical theme: the tension between the actual and the ideal. This gap invites reflection on human striving, imperfection, and the drive to close the gap between what is and what ought to be.
5. Unity in Diversity
The formula aggregates multiple f_i(x) and z_i*, suggesting the philosophical idea of harmonizing multiplicity. Life often involves balancing diverse needs or goals, and this formula formalizes that process by choosing the greatest discrepancy as the focal point.
Conclusion
In essence, this formula could symbolize a pragmatic approach to imperfection, urging us to focus on the most critical shortcomings while respecting the differing weights of various priorities. It invites reflection on how we allocate our attention and resources in a world of competing demands.
